Introduction
An inverter transformer is an essential component in modern electrical systems that convert DC (Direct Current) to AC (Alternating Current) or vice versa. It is a type of transformer that is specifically designed to handle high-frequency and high-voltage signals.

Inverter transformers are critical in the operation of power inverters, solar inverters, uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, and welding equipment. In this article, we will discuss the importance of inverter transformers, their components, how they work, their applications, advantages, and disadvantages.
Components of an inverter transformer
An inverter transformer comprises three essential components; primary winding, secondary winding, and a core. The primary winding is the input side of the transformer and is responsible for receiving power from the DC source. The secondary winding is the output side of the transformer, and it is responsible for transmitting power to the AC load. The core is the magnetic component that couples the primary and secondary windings.
III. How an inverter transformer works
An inverter transformer works by converting DC power to AC power. The conversion process involves three primary steps; step-up or step-down voltage transformation, frequency conversion, and pulse-width modulation (PWM) control. First, the transformer steps up or steps down the DC voltage to the required AC voltage level. Next, it converts the DC power to AC power by generating a sinusoidal waveform of the required frequency. Finally, the transformer uses PWM control to regulate the amplitude and duration of the AC waveform.

Applications of inverter transformers
Inverter transformers have a wide range of applications in various electrical systems. Some of the most common applications include power inverters, solar inverters, UPS systems, and welding equipment. Power inverters convert DC power from batteries or other sources to AC power for use in homes, cars, and other applications. Solar inverters convert DC power from solar panels to AC power for use in homes and businesses. UPS systems provide backup power to critical loads during power outages. Welding equipment uses inverter transformers to convert low voltage DC power to high voltage AC power for welding purposes.
Advantages of using inverter transformers
Inverter transformers offer several advantages over traditional transformers. Firstly, they are more energy-efficient since they can operate at higher frequencies, reducing energy losses due to core saturation. Secondly, they are smaller and lighter in size, making them ideal for use in portable applications. Thirdly, they offer better power quality, reducing the risk of power surges and fluctuations that can damage sensitive equipment. Finally, they are less expensive than traditional transformers, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious consumers.
Disadvantages of using inverter transformers
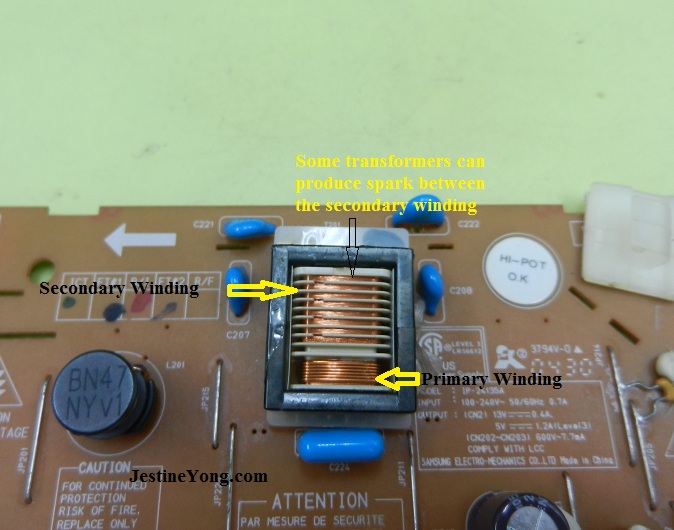
Despite their advantages, inverter transformers also have some disadvantages. Firstly, their design is more complex than traditional transformers, making them more difficult and expensive to manufacture. Secondly, they can generate high-frequency noise that can interfere with other electrical equipment. Finally, they require more maintenance than traditional transformers due to the high frequency and voltage levels they operate at.
Conclusion
In conclusion, inverter transformers are essential components in modern electrical systems that convert DC power to AC power. They consist of three essential components; primary winding, secondary winding, and a core. The transformation process involves three primary steps; step-up or step-down voltage transformation, frequency conversion, and PWM control. Inverter transformers have a wide range of applications, including power inverters, solar inverters, UPS systems, and welding equipment. They offer several advantages, including improved energy efficiency, smaller size, better power quality, and lower cost. However, they also have some disadvantages, including complexity in design, high-frequency noise, and higher maintenance requirements. Despite their disadvantages, inverter transformers remain a critical component in modern electricalsystems, and future developments are likely to improve their performance and expand their potential applications.
In terms of future developments, advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques are expected to improve the performance and reliability of inverter transformers. For example, the use of nanocrystalline alloys in transformer cores has been shown to reduce energy losses and improve efficiency. Similarly, advancements in surface mount technology have made it possible to produce smaller and more reliable inverter transformers.
Potential applications for inverter transformers are also expanding as new technologies emerge. For example, the growing demand for electric vehicles is driving the development of high-power inverter transformers capable of handling the large current loads required by these vehicles. Similarly, the increasing use of renewable energy sources like wind and solar is creating new opportunities for inverter transformers to enable the integration of these sources into the grid.
In conclusion, inverter transformers are critical components in modern electrical systems that enable the efficient and reliable conversion of DC power to AC power. They offer several advantages over traditional transformers, including improved energy efficiency, smaller size, better power quality, and lower cost. However, they also have some disadvantages, including complexity in design, high-frequency noise, and higher maintenance requirements. Advances in materials science and manufacturing techniques are likely to improve their performance and reliability, while new technologies are expanding their potential applications. Overall, inverter transformers are an essential technology that will continue to play a critical role in meeting the energy needs of modern society.
Inverter transformers have become an essential technology in today’s world, with their widespread use in various industries ranging from power generation, transmission, and distribution, to industrial and residential applications. One of the main reasons for their popularity is their ability to provide efficient power conversion, which is necessary for the operation of a wide range of electrical devices.
One significant advantage of inverter transformers over traditional transformers is their ability to operate at higher frequencies. This enables them to provide better power quality, as well as improved energy efficiency. Inverter transformers typically operate at frequencies between 20 kHz and 100 kHz, whereas traditional transformers typically operate at 50 or 60 Hz. This higher frequency allows for smaller and lighter transformers, which is particularly useful in applications where space is limited.
Inverter transformers are also commonly used in solar power systems, where they are used to convert the DC power generated by solar panels into AC power that can be used by homes and businesses. These systems typically require a step-up transformer to increase the voltage of the power generated by the panels to a level that is suitable for transmission and distribution.
See Also-
- Best 2000 Watt Inverter 2023
- Best 3000 Watt Inverter 2023
- Best 3500 Watt Inverter Generator 2023
- Best 4500 Watt Inverter Generator 2023
- Best Dual Fuel Inverter Generator 2023
